Captive insurance, also known as microcaptive, is an increasingly popular alternative risk management strategy for businesses. By forming their own insurance company, organizations gain more control over their coverage and can potentially unlock a range of unique benefits. One key aspect that has attracted attention is the IRS 831(b) tax code, which allows qualifying companies to enjoy certain tax advantages. In this article, we will delve into the world of captive insurance, exploring its potential advantages, its alignment with the IRS 831(b) tax code, and how businesses can leverage this innovative strategy to better protect their assets and drive financial success. So, let’s dive in and discover the many benefits of captive insurance.
Understanding Captive Insurance
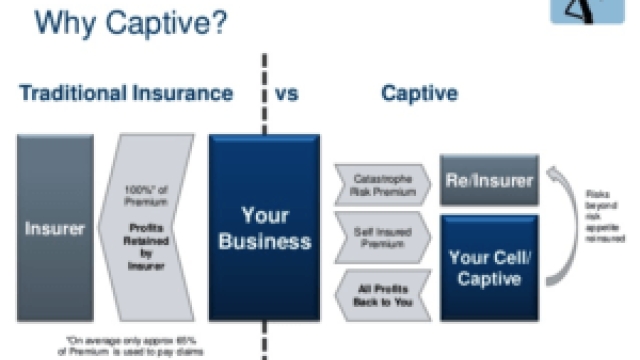
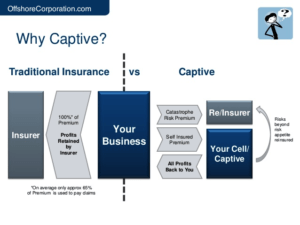
Captive insurance is a risk management strategy that allows businesses to create their own insurance company to cover their specific risks. By forming a captive insurance company, businesses can gain more control over their insurance coverage and potentially benefit from financial advantages.
One commonly used section of the tax code that relates to captive insurance is IRS 831(b). Under this tax provision, small captive insurance companies can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, while their premium income is excluded from taxation. This can provide significant tax advantages for businesses using captive insurance.
Microcaptive insurance refers to smaller captive insurance companies that are usually owned by a single business or a group of related businesses. These microcaptives often serve as a cost-effective alternative to traditional insurance policies, allowing businesses to customize their coverage to their specific needs.
Understanding captive insurance and its various components, such as IRS 831(b) and microcaptives, is essential for businesses looking to explore the benefits of this risk management strategy. By delving into the specifics of captive insurance, businesses can make informed decisions about whether it aligns with their insurance needs and could potentially offer advantages over traditional insurance options.
Exploring the IRS 831(b) Tax Code
In the world of captive insurance, the IRS 831(b) tax code plays a significant role. This particular section of the tax code has gained attention for its potential benefits for small and mid-sized businesses looking to establish captive insurance companies.
At its core, the IRS 831(b) tax code provides an opportunity for these businesses to enjoy certain tax advantages by forming a captive insurance company. Under this provision, captive insurance companies that meet specific criteria can be classified as a "microcaptive" and benefit from favorable tax treatment.
By electing to be taxed under section 831(b) of the IRS tax code, these microcaptives can pay taxes only on their investment income instead of the premiums received. This tax advantage allows businesses to retain more of their earnings within the captive, providing potential opportunities for growth and increased financial stability.
Overall, the IRS 831(b) tax code has become a focal point for businesses looking to explore the advantages of captive insurance. Through this provision, small and mid-sized companies have the potential to unlock benefits that can help them navigate the complexities of risk management while also optimizing their financial strategies.
Benefits of Microcaptive Insurance
Microcaptive insurance, as defined by the IRS 831(b) tax code, offers a range of benefits for businesses. Here, we explore some of the advantages that captives provide.
Increased Risk Management Control:
Captive insurance allows businesses to have more control over their risk management strategies. By establishing their own insurance company, businesses can tailor insurance policies to suit their specific needs. This gives them the freedom to choose the coverage and limits that best protect their unique risks, rather than relying on traditional insurance providers.
Potential Cost Savings:
One of the key benefits of microcaptive insurance is the potential for cost savings. By retaining risk and forming their own captive, businesses may reduce their insurance costs over time. This is because they can eliminate expenses associated with traditional insurance overhead, such as marketing, profit margins, and administrative fees. Additionally, captives may offer more stable premiums, providing businesses with greater financial predictability.
Microcaptive
Improved Cash Flow:
Microcaptive insurance can also positively impact a company’s cash flow. In traditional insurance models, premiums are paid to third-party insurers, which may then invest those funds until claims are paid out. With a captive, the premiums paid by the company are held within the captive, allowing the business to potentially earn investment income on those funds. This increased cash flow can provide additional financial stability and flexibility for the company.
In conclusion, microcaptive insurance brings several benefits, including increased risk management control, potential cost savings, and improved cash flow. By exploring captive insurance options under the IRS 831(b) tax code, businesses can unlock these advantages and better protect themselves against the risks they face.